Table of Contents
- Prerequisites
- Install Copilot Studio extensions.
- Connect your Copilot Studio bot to an omnichannel instance
- Configure your Copilot Studio bot in the admin app
- Enable a human agent to transfer a conversation back to a bot
- Configure context variables for the Copilot Studio bot
- Automatically close a conversation.
- End bot conversation
- Configure the CoPilot Studio bot in Omnichannel Administration
- Conclusion
Omnichannel for Customer Service augments the functionality of Dynamics 365 Customer Service Enterprise by offering many features. These features empower organizations to establish immediate and interactive communication with their clientele via diverse digital messaging platforms. However, an additional license is mandatory to utilize Omnichannel for Customer Service.
Microsoft Copilot Studio is a tool that facilitates organizations in automating standard dialogues, enabling service agents to focus on interactions of higher value. When a conversation is upgraded from a bot to a human agent, the agent can view the complete transcript of the Bot’s conversation. This lets the agent understand the context while engaging with the customer thoroughly.
When you integrate a Copilot Studio bot with Omnichannel for Customer Service, you gain the following capabilities for bot conversations:
-
Seamlessly incorporate your Bot across all communication channels, eliminating the necessity for channel-specific coding within the Bot itself.
-
Transition bot dialogues to human agents, ensuring the entirety of the conversation’s context is included for a seamless customer experience.
-
Post-chat, scrutinize the Bot’s conversation transcript, conveniently stored in Microsoft Dataverse, to gain insights and improve future interactions.
-
Establish routing protocols that strategically direct incoming inquiries to bots based on specific contexts, such as the nature of the issue or the type of customer. For instance, you could direct less complex issues to bots or guide the conversation toward a sales or support bot, contingent on the customer’s website browsing history.
-
Monitor bot interactions in real-time utilizing the supervisor dashboard, which provides comprehensive details, including customer sentiment.
-
Leverage historical dashboards to extract valuable insights into bot performance. This can be achieved through critical metrics such as resolution rate, escalation rate, time taken for resolution or escalation, and average sentiment.
Prerequisites
Before integrating Copilot Studio bots into Omnichannel for Customer Service, ensure the following:
-
You must have:
-
A product license for Copilot Studio.
-
Depending on your business requirements, a product license for chat, digital messaging, or voice channel for Dynamics 365 Customer Service.
-
-
You must hold the Omnichannel administrator role.
-
An application must be registered on the Azure portal before connecting to Omnichannel for Customer Service.
-
You must possess a preconfigured bot that integrates with Omnichannel for Customer Service.
Install Copilot Studio extensions.
Copilot Studio provides a streamlined mechanism for transitioning voice and text-based dialogues to human agents. This is achieved using various communication mediums such as chat, digital messaging, and voice channels, all integrated within Dynamics 365 Customer Service. To facilitate your Bot’s ability to transfer conversations to the omnichannel interface, installing the Copilot Studio extension solutions specifically designed for Dynamics 365 Customer Service is essential.
To accomplish this, follow these steps:
-
Ensure the prerequisites are met.
-
Verify the successful installation of the extension solutions by checking for the presence of the extension solution variables in Copilot Studio.
Connect your Copilot Studio bot to an omnichannel instance
In Microsoft Copilot Studio, edit your Bot. Select Settings and Customer Engagement Hub in the navigation menu, then choose the Omnichannel tile.
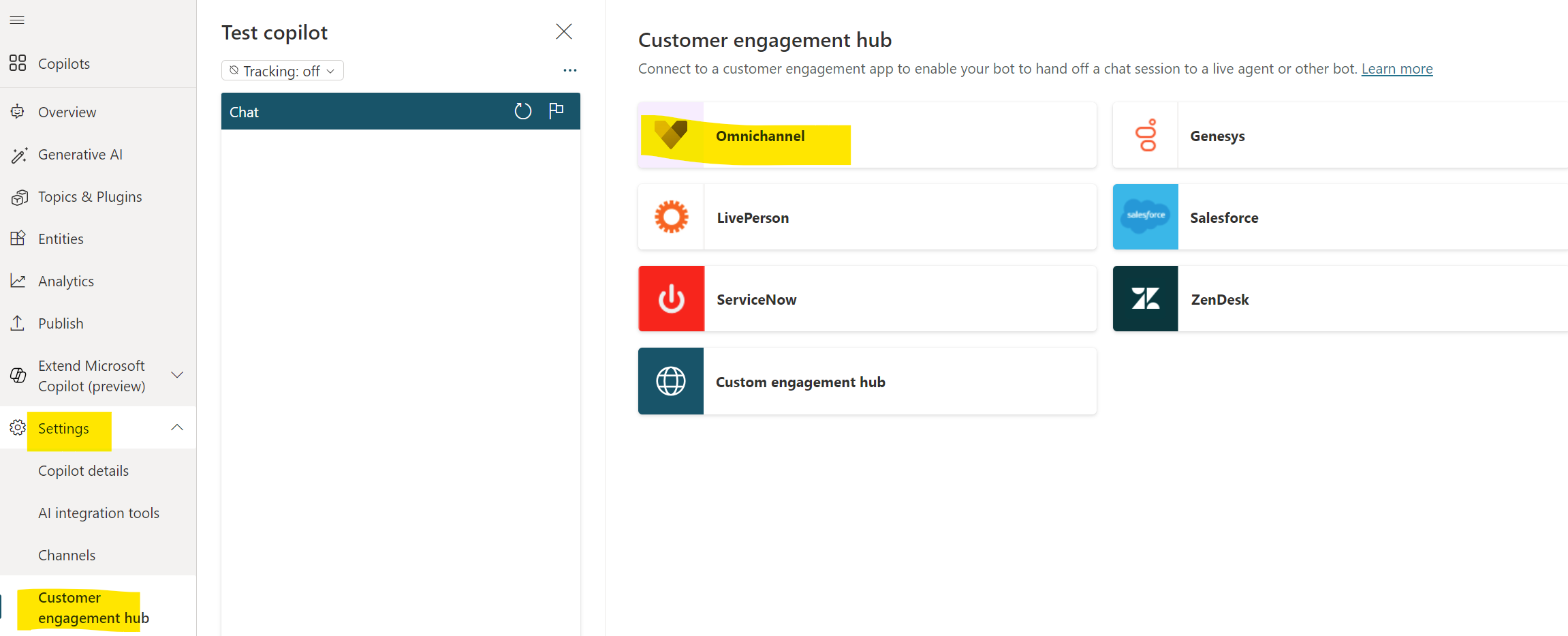
Click Connect.
-
The Omnichannel installation must be in the same environment as the Bot.
-
If you’re using Application Lifecycle Management (ALM), you may see a message stating that we cannot determine if Omnichannel for Customer Service integration is enabled for the environment.
Configure your Copilot Studio bot in the admin app
Within the Customer Service admin center application, navigate to the Workstreams section to find a list of bots. From this list, select the Copilot Studio bot. This action enables the Bot to transition conversations to human agents. See below.
Enable a human agent to transfer a conversation back to a bot
In certain customer support situations, it may be necessary for a human agent to transition a conversation back to a Copilot Studio bot after delivering personalized support. This handoff from a human agent to a bot can be beneficial in providing additional assistance with routine, repetitive tasks or collecting more data, such as during a customer feedback survey.
There are two methods to facilitate the transition of a conversation from a human agent back to a bot:
-
Establish two bots that are located in two distinct queues. This setup allows for a clear division of responsibilities between the bots, with each Bot handling specific tasks within its queue.
-
Set up two bots within the same queue. This configuration allows for a seamless transition between bots, as they operate within the same queue, making sharing and managing conversations easier.
Two bots in two queues
In this scenario, a bot transfers a conversation to a human agent, who then transfers the conversation to another bot in a different queue.
-
The process begins when a customer initiates a dialogue.
-
This dialogue is then directed towards Queue 1.
-
The initial Bot, Bot A, acknowledges and engages in the conversation.
-
At some point, the customer wants to communicate with a human agent.
-
Subsequently, the conversation is transitioned to a human agent who is also part of Queue 1.
-
The customer and the human agent engage in a dialogue.
-
Upon providing the necessary support, the human agent transfers the conversation to a second bot, Bot B, in Queue 2.
-
The human agent is then disengaged from the conversation.
-
The system then routes the conversation to Bot B in Queue 2.
-
Upon receiving the conversation, the system prompts Bot B to send a greeting message to the customer.
-
Finally, the customer engages in a dialogue with Bot B
Two Bots in One Queue
In this scenario, once the agent’s task is completed, a conversation is transferred from a bot to a human agent and then from the human agent to another bot within the same queue. To ensure a seamless flow of conversation, it is recommended to configure the first Bot (Bot A) and the human agent with the highest capacity. In contrast, the second Bot (Bot B) should be set with the lowest capacity.
The process unfolds as follows:
-
A customer initiates a conversation and is then directed to a specific queue.
-
Having the highest capacity, Bot A acknowledges and engages in the conversation.
-
The customer expresses a desire to communicate with a human agent.
-
The conversation is then transitioned to a human agent with the second-highest capacity within the queue.
-
The customer and the human agent engage in a dialogue.
-
Upon providing the necessary support, the human agent transfers the conversation to Bot B within the same queue.
-
The human agent is then disengaged from the conversation, and the conversation is directed to Bot B.
-
Bot B receives the messages in the following sequence:
-
A conversation update indicating that the “Bot is added”
-
The Omnichannel Set context event
-
-
The system then prompts Bot B to send a greeting message to the customer.
-
Finally, the customer engages in a dialogue with Bot B.
Configure context variables for the Copilot Studio bot
You can set up context variables after successfully integrating your Bot into a workstream. These variables are crucial in routing work items, ensuring that each item reaches the appropriate destination within your workflow.
Moreover, you can enhance the functionality of your Copilot Studio bot by sharing context from Omnichannel. This context-sharing allows your Bot to provide a more enriched and personalized user experience. It enables the Bot to understand the user’s journey better, respond to queries more accurately, and deliver a more tailored service, improving overall customer satisfaction.
See Configure context variables for Copilot Studio bot for details.
Automatically close a conversation.
When a bot handles a conversation that has not been escalated to a human agent, it will be automatically terminated if the customer discontinues or abandons it. Furthermore, the system is designed to automatically close any inactive discussion for 30 minutes to manage resources effectively.
Once a conversation is closed, its status will be updated across various platforms. Specifically, on the Omnichannel for Customer Service dashboard, the conversation will be marked as ‘Closed.’ Simultaneously, the conversation’s status will be updated to ‘Resolved/abandoned’ on the Copilot Studio dashboard. This ensures consistency in tracking and managing customer interactions across different platforms.
End bot conversation
To ensure a smooth and controlled end to a conversation, it is necessary to configure your Copilot Studio web application bot to terminate a conversation when required.
An additional step is required once a customer decides to close the chat window. You need to set up a context variable that will explicitly signal the end of the conversation in the Omnichannel for Customer Service platform.
To achieve this in Copilot Studio, follow these steps:
-
Choose the Bot you wish to configure and add a new topic.
-
Click on ‘Go to authoring canvas’ and then select ‘Add node.’ In the dropdown menu, choose ‘Call an action,’ followed by ‘Create a flow.’
-
A new tab will open, taking you to the Power Automate window. Here, you need to:
-
Locate the ‘Return value(s) to Copilot Studio’ box and click ‘Add an Output.’ From the options, select ‘Yes/No.’
-
In the ‘Enter title’ box, type ‘CloseOmnichannelConversation,’ which is the name of the Omnichannel for the Customer Service context variable.
-
Switch to the’ Expression’ tab in the ‘Enter a value to respond’ box. Type ‘bool(true)’ to construct the expression and confirm by clicking ‘OK.’
-
-
Save all changes made and close the Power Automate window.
-
Return to the topic you were editing in Copilot Studio. Select ‘Call an Action’ again, and from the list, choose the flow you just created.
-
Finally, in the ‘Add node’, select ‘End the conversation’, followed by ‘Transfer to the agent’.
Following these steps ensures that your Bot is appropriately configured to end a conversation when a customer closes the chat window, providing a seamless and controlled user experience.
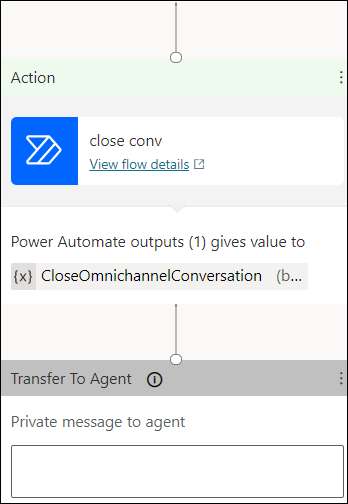
-
Navigate to the topic where you need to trigger the conversation-ending topic in Omnichannel for Customer Service and use the Go to another topic option in Add a node.
-
Choose the topic you created for ending the bot conversation.
-
Save and publish the changes.
Configure the CoPilot Studio bot in Omnichannel Administration
Once you have successfully created and configured your Power Virtual Agents bot to function with Omnichannel for Customer Service within the Omnichannel Administration, you can further enhance its capabilities by setting it up to transfer conversations to queues. To ensure the Bot can receive incoming messages, it is mandatory to be associated with one queue. The Bot will then adhere to the routing rules defined during the setup process.
To connect your Bot to the Omnichannel for Customer Service, follow these steps:
-
Navigate to the Omnichannel Administration application.
-
Assign your Bot to an existing queue. This step is crucial as it allows your Bot to receive and manage incoming messages.
-
Once you’ve completed the assignment, select ‘Done’.
After completing these steps, you will be redirected to the bot profile page. Here, you can verify that your Bot is successfully connected and ready to operate.
Your Bot is fully equipped to accept and respond to customer-initiated conversations, providing a more efficient and streamlined customer service experience.
Create a bot queue and a human agent queue.
To ensure efficient handling of customer queries, you must set up a workstream, create context variables, and establish routing rules for human and virtual agents. Here’s a detailed guide on how to do this:
-
-
Workstream Selection or Creation: Start by selecting an existing workstream or creating a new one. A workstream is a defined set of processes that manage your organization’s work flow.
-
Context Variables Creation: Next, create context variables. These are crucial as they are used during setup to enable the Bot to handle customer queries effectively. A context variable is a dynamic placeholder that stores specific data, which is used to route incoming customer queries to the appropriate bots and agents.
-
Routing Rule Creation for Human Agent: Create a routing rule specifically for the human agent and incorporate it into the workstream. A routing rule is a set of conditions determining how incoming queries are directed within the system.
-
Routing Rule Creation for Virtual Agent: Similarly, create a routing rule for the virtual agent and add it to the workstream. This rule will guide the system on how to direct queries that are meant for the virtual agent.
Routing rules are essential to guide incoming customer queries to their respective queues. Each routing rule consists of a condition and a destination queue. The customer query is directed to the designated queue if the condition is met. For bots, the condition is constructed using the context variable.
Bots are programmed to be the first point of contact for customer queries. They gather information about the query and, if necessary, pass the query on to a human agent. To facilitate this behavior, you must add a bot user to the queue and configure routing rules so incoming customer queries are directed to the queue with the bot user.
Lastly, ensure the routing rules are correctly mapped to the appropriate queues. This step is crucial for routing queries accurately and efficiently.
-
Note
When you run a report on Copilot Studio activity, the number of bot sessions may differ from the number of sessions in Omnichannel for Customer Service.
Set escalation rules
To guarantee that your Bot accurately routes customer inquiries to the proper agent, you can set up escalation rules in two distinct ways:
-
Incorporate the Bot into an Existing Human Agent Queue: This method involves integrating the Bot into an existing queue designated for human agents. The advantage of this approach is that it doesn’t require any modifications to your current routing rules. The existing rules will guide incoming messages to the Copilot Studio bot. When an escalation or handoff is initiated, the customer will be transitioned from the Copilot Studio bot to the human agent by the pre-established escalation routing rules.
-
Establish Separate Queues for the Bot and Human-Agent: This approach involves creating two distinct queues - one for the Bot and another for the human agent. In this scenario, you must set up workstreams that include context variables and suitable routing rules to direct customer queries accurately. This method provides more flexibility and control over the routing process but requires more initial setup.
By choosing the method that best suits your organization’s needs, you can ensure that your Bot effectively routes customer queries to the appropriate agent, enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of your customer service operations.
Conclusion
Integrating a Copilot Studio bot with Dynamics 365 Customer Service can significantly enhance customer engagement by automating routine conversations. This setup allows for effortless integration across various channels and enables seamless transfer of conversations between bots and human agents. Businesses can gain valuable insights into bot performance and customer interactions by leveraging features like real-time monitoring, historical dashboards, and context variables. Additionally, implementing escalation rules and configuring the Bot to end conversations appropriately ensures efficient handling of customer queries. However, to successfully achieve this integration, it’s essential to meet the prerequisites, install the required extensions, and correctly set up the Bot in the Omnichannel environment.





Start the conversation