Table of Contents
Content Classification
Content for IT architects - Level 100 (Background & Integration knowledge)
Summary Lede The Copilot Studio extension for VS Code enables developers to create, edit, and manage AI agents directly in their favorite code editor. Bringing features like IntelliSense, version control integration, and cloud synchronization to agent development bridges the gap between traditional software development and conversational AI creation, making the process more efficient and accessible to technical teams. This helps streamline the development with a codeview.
Copilot Studio (Preview) is a Visual Studio Code extension developed by Microsoft to streamline creating and managing custom agents within the VS Code environment. By integrating with Microsoft Copilot Studio (the platform for building and orchestrating agents), this extension lets developers work on AI agent components (such as knowledge sources, actions, topics, and triggers) using VS Code’s powerful editing features.
This is not to be confused with GitHub Copilot (an AI coding assistant for general programming tasks); instead, the Copilot Studio extension is a specialized tool for editing agents — essentially the brains behind custom AI assistants built for Microsoft 365 and other ecosystems.
Overall Benefit: The Copilot Studio extension brings the comfort and productivity of VS Code to agent development. It offers syntax highlighting, IntelliSense autocompletion, source control integration, and direct cloud syncing, which significantly improve efficiency and accuracy when developing agents. This article will explore the extension’s key features, benefits, and common usage scenarios, demonstrating how developers can leverage it to build and refine assistants.
Overview of Copilot Studio Extension
The Copilot Studio VS Code extension is designed to enhance the development experience of Microsoft Copilot Studio agents. In practical terms, it brings the agent-authoring capabilities of the web-based Copilot Studio into Visual Studio Code. After installing the extension, developers can sign in to their Copilot Studio environment and retrieve a list of agents associated with their account within VS Code. Each agent can be cloned (downloaded) into a local folder, where its components (configurations, knowledge bases, triggers, etc.) become editable files.
Key aspects of the extension’s integration with VS Code
Dedicated Sidebar: The extension adds a Copilot Studio icon to VS Code’s sidebar. Clicking it opens panels for connecting to your Copilot environment and managing agents. Agent File Structure: An agent is represented as a collection of files (often in YAML format) for different components – e.g., definitions of conversational topics, triggers for those topics, actions the agent can perform, and knowledge sources it can draw from. This logical structure is visible and navigable in VS Code’s explorer. Live Connection: The extension maintains a live connection to the cloud service. Instead of editing a local copy in isolation, you are editing a cloud-backed project. Changes can be pulled from or pushed to the server on demand, ensuring your local copy and the cloud agent stay in sync.
By providing this tight integration, the extension transforms VS Code into a development environment for agents, complementing the web studio with a coder-friendly interface.
Key Features and Functionalities
- Intelligent Editing with IntelliSense: One of the standout features is full language support for agent configuration files. Since these are often YAML (a format for defining agent logic and connections), the extension offers IntelliSense code completion and suggestions as you edit. This means that as you type keys or values (for example, adding a new knowledge source or defining a trigger condition), VS Code will auto-suggest valid options and syntax, reducing errors. It even provides guided tips for the agent schema, helping you follow best practices in defining your agent. In short, the extension makes editing complex AI agent configs as convenient as writing standard code.
- In-Editor Authentication and Agent List: Upon first use, the extension prompts you to sign in to your Copilot Studio environment (using your organizational or Microsoft account). Once authenticated, a panel in VS Code will display all available agents in your environment. You can easily browse and select the agent you want to work on. This direct integration eliminates manual export/import steps – you’re working with the real agents from your environment.
- Clone, Pull, and Push (Source Control Integration): The extension enables three core operations to manage agent content, akin to source control workflows
- Clone Agent: One click can clone an existing agent from the cloud to your local machine. This pulls all the agent’s components (knowledge files, action definitions, etc.) into a local workspace folder. (A similar structure is created locally from scratch if you start a new agent.)
- Pull Changes: If someone on your team or another system has updated the agent via Copilot Studio (web) or another VS Code session, you can fetch and pull the latest changes to update your local files. This ensures you’re always working on the current version of the agent. In VS Code, Fetch and Pull buttons (familiar from Git workflows) are available in the Copilot Studio panel.
- Push Changes: After editing, you can push your local modifications back to the cloud with a click. The extension uses VS Code’s source control interface to show outbound changes, which will instantly apply to the agent in Copilot Studio. This provides a live editing experience – no separate deployment step is needed; when you push, the agent’s cloud configuration updates immediately.
- Authoring Tools and Validation: Because the extension leverages VS Code’s capabilities, developers benefit from features like search across files, diff views to see changes before pushing, and basic validation. VS Code will flag YAML syntax errors or formatting issues in real-time. For instance, if you forget a colon or indent incorrectly, you’ll see a squiggly underline, helping you fix the configuration before it causes problems at runtime. While the extension is a preview, it improves authoring confidence by catching mistakes early.
- Multi-Agent Management: If your organization has multiple agents, for different departments or use cases, the extension helps manage them in one place. You can switch between agents in the sidebar and clone or open another agent without leaving VS Code. This benefits developers overseeing several AI assistants; for example, you might simultaneously maintain a customer support bot and an HR assistant. The extension gives a unified view of all, which the web interface might silo separately.
- Platform and Language Support: The extension focuses on editing the configuration of Copilot Studio agents rather than writing traditional program code. Therefore, it supports the domain-specific languages and formats used by Copilot Studio (primarily YAML for declarative agent definitions). If an agent’s actions involve code (for instance, calling an Azure Function or logic app), those may be referenced rather than authored directly in YAML. However, you can still use VS Code to edit any embedded code or scripts as needed. Notably, because VS Code is a multi-language IDE, developers can take advantage of other extensions (including GitHub Copilot or language linters) side-by-side when writing any custom code as part of an agent’s functionality. Essentially, the Copilot Studio extension isn’t limited to one programming language, as it’s agnostic to whether your agent uses Power Fx formulas, JSON definitions, or other config files – all are handled as text in the editor.
Benefits of Using Copilot Studio Extension
- Familiar Development Environment: Working in VS Code means developers can use tools and workflows they already know. Instead of a web form or custom portal, you interact with your agent’s definition as if it were code. This familiarity can dramatically improve productivity. For example, features like code folding, find-and-replace across files, or integration with your favorite VS Code themes and settings make editing more comfortable and efficient. The extension lowers the learning curve for software developers to adopt Copilot Studio by bringing the AI agent config into a code editor.
- Faster Configuration with Fewer Errors: The IntelliSense and real-time validation reduce the chance of mistakes. Autocompletion means you don’t have to memorize exact property names or syntax for triggers and actions – the extension suggests them. This speeds up writing and ensures correctness (e.g., it’s less likely to miss a required field or use an unsupported value). Over time, this can lead to more robust agents because the configuration is done right the first time. It’s akin to having an intelligent assistant looking over your shoulder as you configure your bot.
- Instant Feedback and Iteration: With the extension, the cycle of making a change and seeing its effect is much shorter. Traditionally, one might edit an agent in a web interface, save it, and test it. In VS Code, you can edit multiple files rapidly, push all changes simultaneously, and immediately test the updated agent in the Copilot Studio testing chat (or wherever the agent is surfaced). The fetch/pull mechanism also means that if a teammate made updates (or if you made quick fixes via the web UI), you can integrate those changes into your local session seamlessly. This encourages an agile, iterative development style for AI agents that is closer to how one would refine software code.
- Better Organization and Version Control: Because agent components appear as files, you can leverage version control practices. Even though the Copilot Studio extension uses an internal sync (not Git), nothing stops you from managing the cloned agent folder in a Git repository for backup or collaboration. Advanced users can connect the folder to a source control system to track changes over time. Team collaboration improves as you can share configuration changes via Git or by multiple people cloning and pushing via the extension (with coordination). Also, a local copy gives you an offline record of the agent’s state, enabling code reviews for changes or rollbacks if needed.
- Leverages VS Code Ecosystem: Running inside VS Code means you can use extensions and tools like any other project. Need to edit JSON from a knowledge connector? VS Code’s JSON formatter can help. Want AI help while writing a complex regex in a trigger? GitHub Copilot (if you have it enabled) could assist. The Copilot Studio extension benefits from and contributes to the rich VS Code ecosystem, making AI agent development more powerful.
Connect to Copilot Studio for the first time
-
Select the Copilot Studio icon in the primary side bar of Visual Studio Code. The extension asks for your permission to sign in.
-
Select Allow, and sign in with the appropriate credentials for your Copilot Studio environment.
How to use
Clone an agent
(Optional) You can open the desired agent in Copilot Studio and copy its URL from your browser’s address bar.
- In the Copilot Studio panel of Visual Studio Code, select Clone agent.
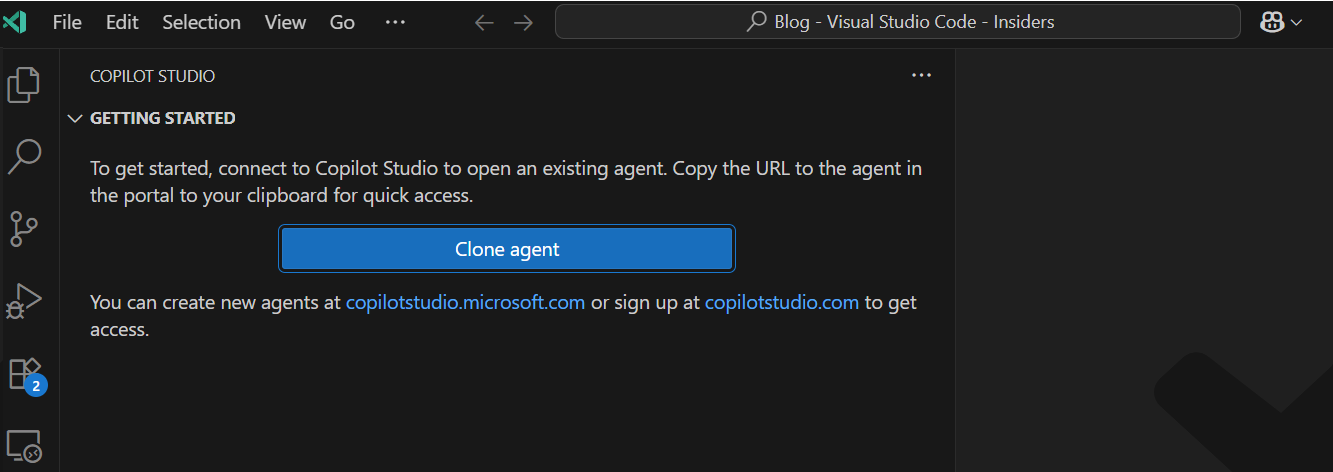
- Select your agent (marked with “from clipboard” if you already copied the URL); otherwise,
- select the desired environment and then select the desired agent.
- The extension prompts you to select a folder to hold your agent’s files (similar to a local repository).

- Select the desired folder.
Edit your agent
To edit any component, open the corresponding file and make the desired changes. Since Visual Studio Code natively supports YAML files, the Copilot Studio extension supports IntelliSense code completion and can provide guided tips. You can also find new elements that are not yet visible in the web interface.

Sync your changes
The Copilot Studio extension uses the same source control features as Visual Studio Code. Fetch changes, Pull changes, and Push changes icons are available in the Explorer and Source Control panels of Visual Studio Code.
- To preview any remote changes from Copilot Studio, use Fetch changes.
- To get all remote changes from Copilot Studio, use Pull changes.
- To push your local changes from Visual Studio Code to Copilot Studio, use Push changes.
When you push changes, they are saved directly to Copilot Studio. This is different from having a local agent instance, which you would then deploy to Copilot Studio. The extension provides a live editing experience of a cloud resource.
Installation hints
If you have installed the extension, but it is not working, you should check your dependencies. The extension requires the following dependencies to be installed: .NET runtime
- click on View > Output in Visual Studio Code
and check the output for the Copilot Studio Language Server.
If you see an error message like “The Copilot Studio Language Server requires the .NET runtime to be installed”, you need to install the .NET runtime. The download link is available in the error message, or you can find it on the .NET download page.
Conclusion
The Copilot Studio extension for Visual Studio Code streamlines working with cloud-hosted agents. By integrating familiar source control features, it allows developers to easily clone, edit, and sync their changes in real time. This eliminates the need for separate deployment steps, making managing and updating cloud resources directly from the code editor simpler.




Start the conversation